The Glory of the Heavens
"The heavens declare the glory of God; the skies proclaim the work of his hands." (Psalms 19:1, NIV)

![Martian sand dunes - JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona/NASA Slide 85 of 86: Gullies on Martian sand dunes, like these in Matara Crater, have been very active, with many flows in the last ten years. The flows typically occur when seasonal frost is present. In this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter we see frost in and around two gullies, which have both been active before. (View this observation to see what these gullies looked like in 2010.) There are no fresh flows so far this year, but HiRISE will keep watching. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 50.3 centimeters (19.8 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 151 centimeters (59.4 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.](https://img-s-msn-com.akamaized.net/tenant/amp/entityid/AAvI2Qj.img?h=416&w=799&m=6&q=60&u=t&o=f&l=f)
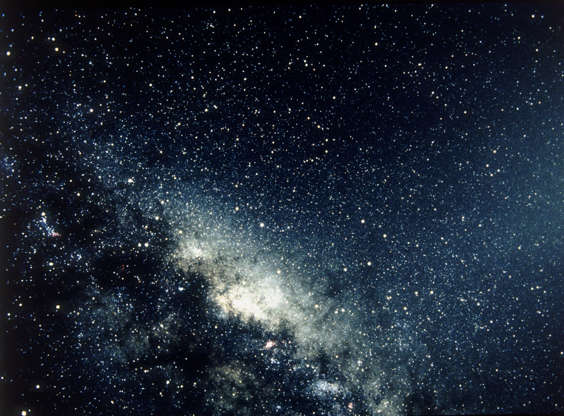





The constellations of (L-R) Ara, Telescopium, Corona Australis and Sagittarius, with the tail of Scorpius on the bottom left, circa 1990.
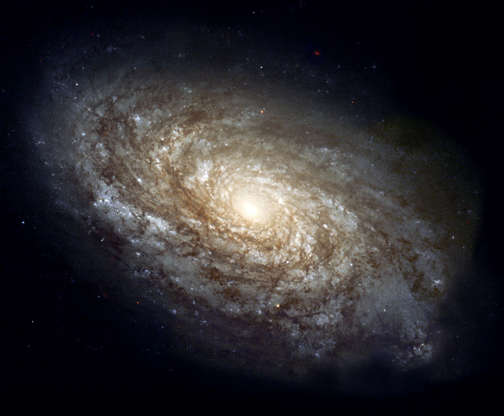
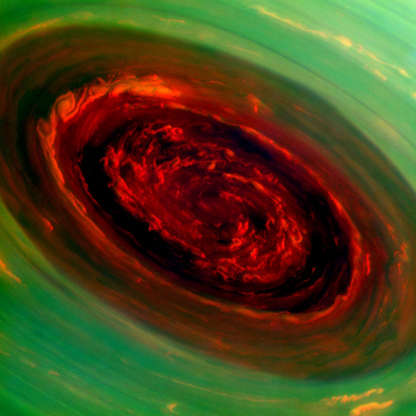
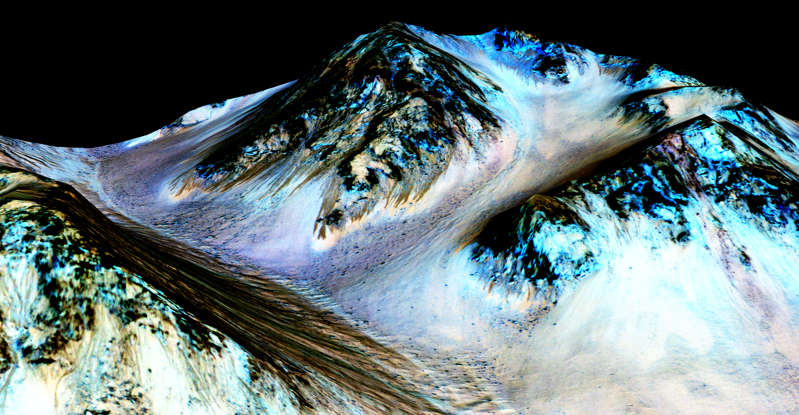
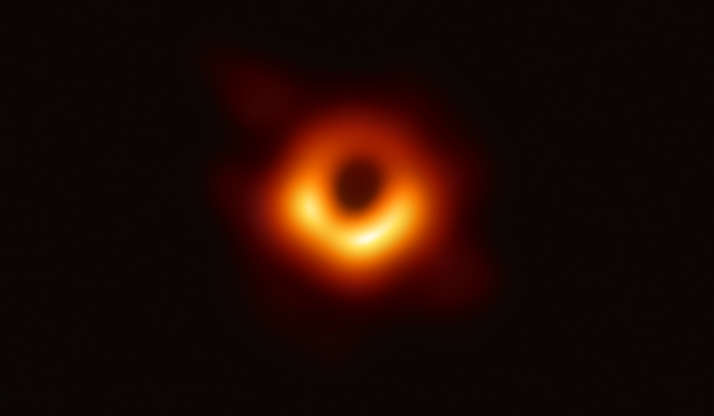














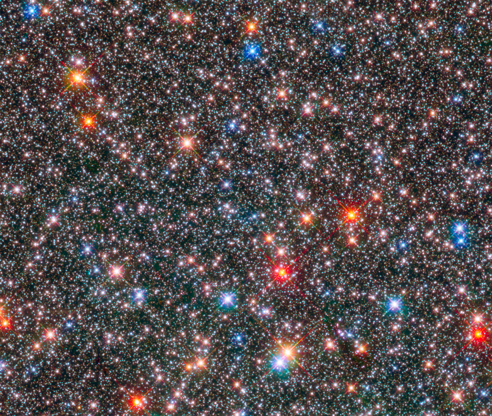
This Hubble Space Telescope image of a sparkling jewel box full of stars captures the heart of our Milky Way galaxy. It's a composite of exposures taken in near-infrared and visible light with Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3.
![Martian sand dunes - JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona/NASA Slide 85 of 86: Gullies on Martian sand dunes, like these in Matara Crater, have been very active, with many flows in the last ten years. The flows typically occur when seasonal frost is present. In this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter we see frost in and around two gullies, which have both been active before. (View this observation to see what these gullies looked like in 2010.) There are no fresh flows so far this year, but HiRISE will keep watching. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 50.3 centimeters (19.8 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 151 centimeters (59.4 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.](https://img-s-msn-com.akamaized.net/tenant/amp/entityid/AAvI2Qj.img?h=416&w=799&m=6&q=60&u=t&o=f&l=f)
Gullies on Martian sand dunes, like these in Matara Crater, as captured from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.

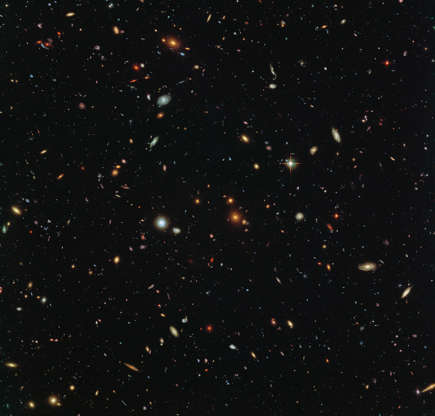
The Hubble Space Telescope reveals thousands of colorful galaxies in space.

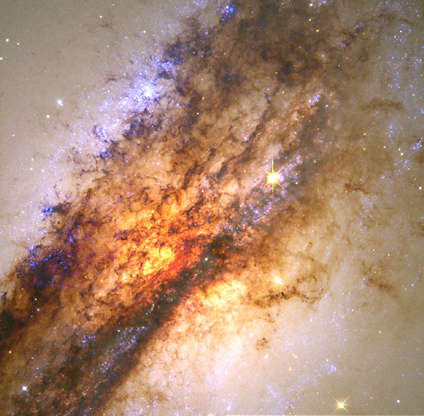
A massive black hole is seen at the center of the galaxy Centaurus A as captured by Hubble Space Telescope.

A composite image of galaxy cluster Stephan's Quintet in the Pegasus constellation, provided by NASA, ESA and Hubble Space Telescope.

A stellar jet in the Carina Nebula is pictured in this undated image provided by NASA, ESA and Hubble Space Telescope.

The constellations of (L-R) Ara, Telescopium, Corona Australis and Sagittarius, with the tail of Scorpius on the bottom left, circa 1990.

The colorful nebula NGC 604 is located in the Triangulum Galaxy which is approximately three million light-years from Earth.
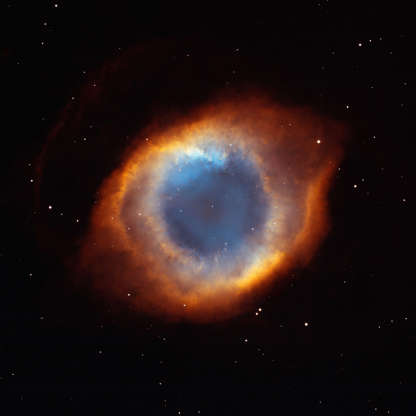

The composite picture of Helix Nebula is a blend of ultra-sharp images from Hubble Space Telescope combined with the wide view of the Mosaic Camera on the National Science Foundation's telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory near Tucson, Arizona, U.S.
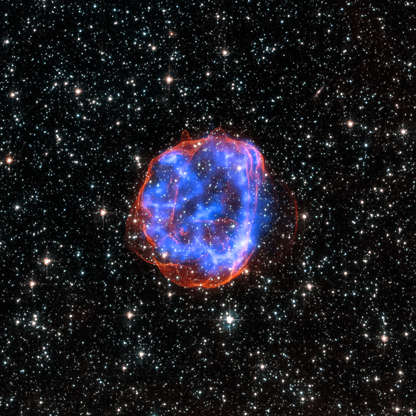


The Hubble Space Telescope captures an expanding shell of debris called SNR 0519-69.0, left behind after a massive star explosion in the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy.
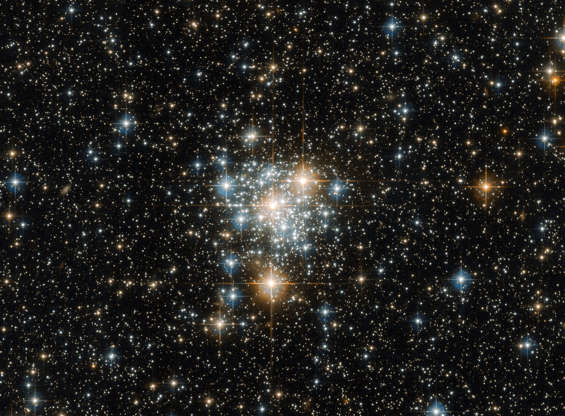


An open star cluster called NGC 299 is seen near Nubecula Minor, a dwarf galaxy near Milky Way.
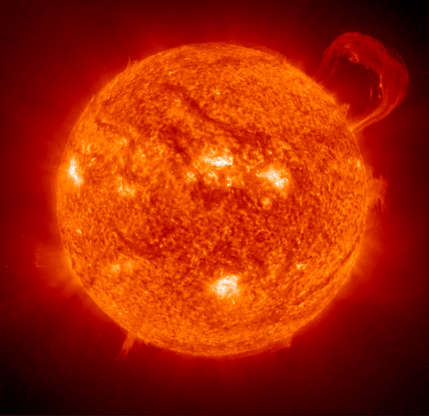


An image of the sun taken by NASA's Extreme Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope and the ESA-operated Solar and Heliospheric Observatory spacecraft.
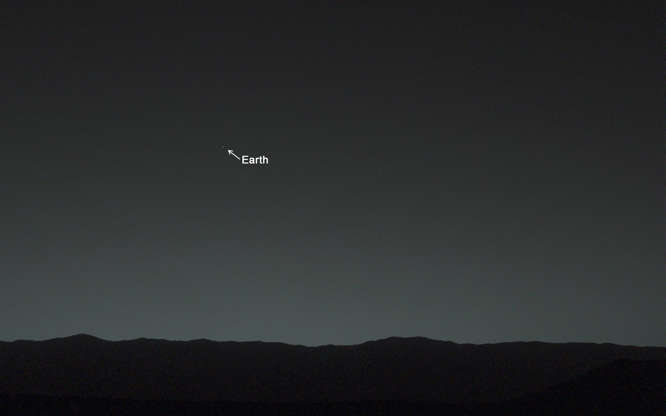


The Curiosity rover took this image of twilight on Mars, with Earth shining as a distinct evening star.

An eclipse of the Sun by Jupiter, as viewed from Galileo spacecraft.
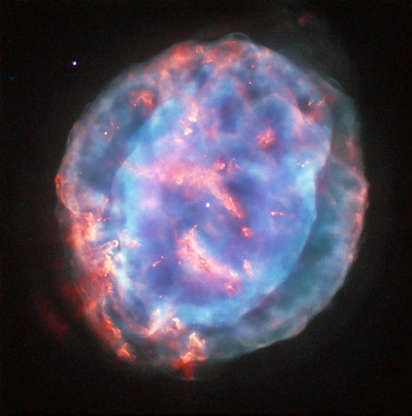


The Little Gem Nebula or NGC 6818 as pictured by Hubble Space Telescope and seen through different colored filters.
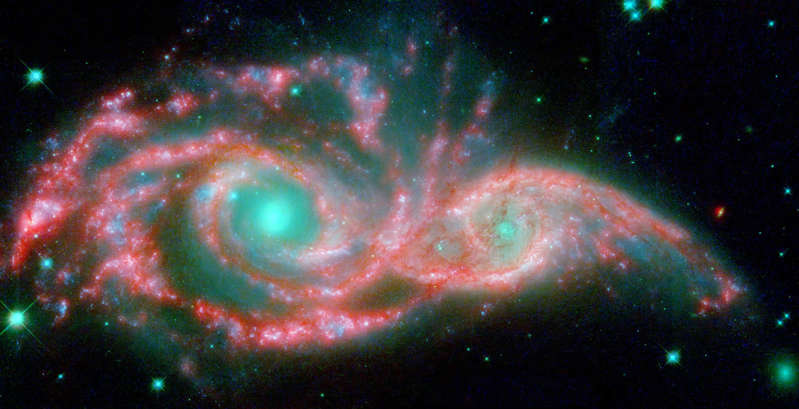


Galaxies NGC 2207 and IC 2163, located 140 million light-years away in the Canis Major constellation, tug at each other, stimulating the formation of new stars.
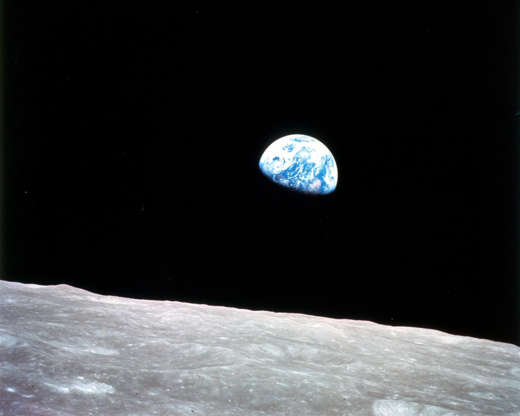


When Apollo 8 entered the lunar orbit on 1968 Christmas Eve, astronauts Commander Frank Borman, Command Module Pilot Jim Lovell and Lunar Module Pilot William Anders held a live broadcast showing pictures of the Earth and Moon as seen from their spacecraft.


The full moon as photographed during NASA's Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, as the astronauts began their journey back to Earth, on July 21, 1969. The spacecraft was already 10,000 nautical miles (18,520 kilometers) from the Moon when the image was taken.
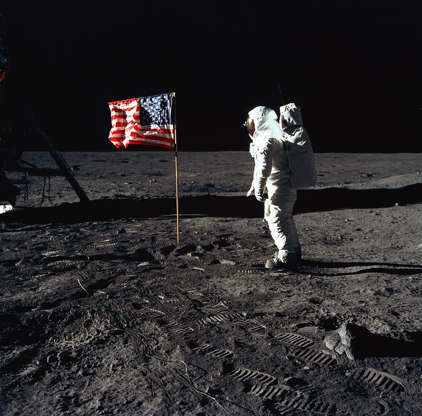


Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., the lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, stands next to a U.S. flag during an Apollo 11 Extravehicular Activity on the surface of the Moon on July 20, 1969.

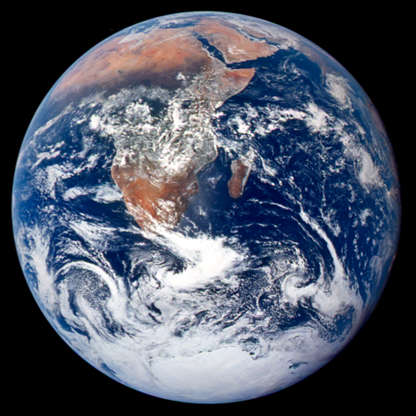
View of the Earth as seen by the crew of Apollo 17 in December 1972.
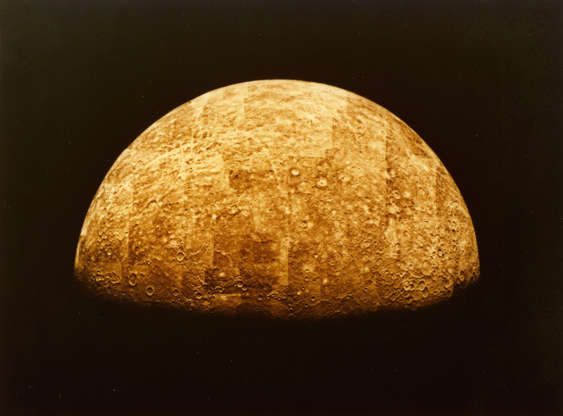


A photomosaic tinted to approximate the appearance of Mercury as seen from the exploratory spacecraft Mariner 10 on March 29, 1974.
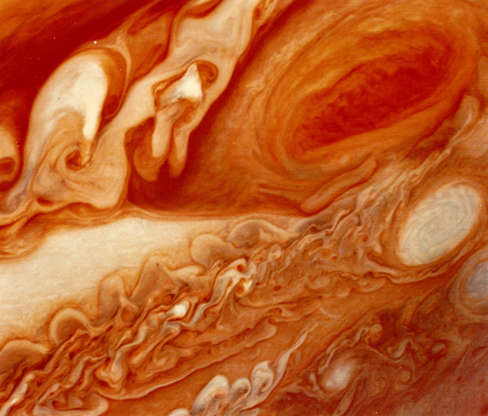


The Great Red Spot on Jupiter and the turbulent region to the west, as seen by Voyager 1 in 1979.

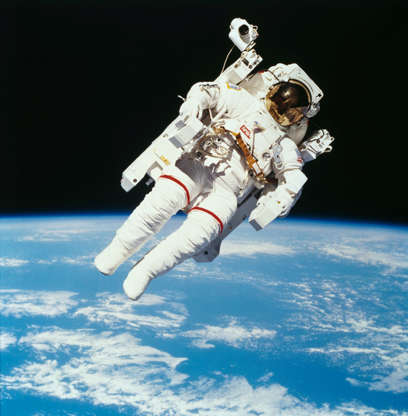
American astronaut Bruce McCandless II photographed from the Space Shuttle Challenger during the first untethered spacewalk in Earth orbit on Feb. 7, 1984.
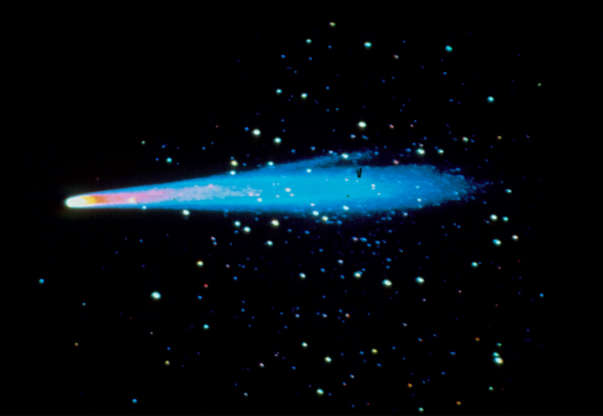


Halley's Comet photographed by the Soviet probe Vega in 1986.

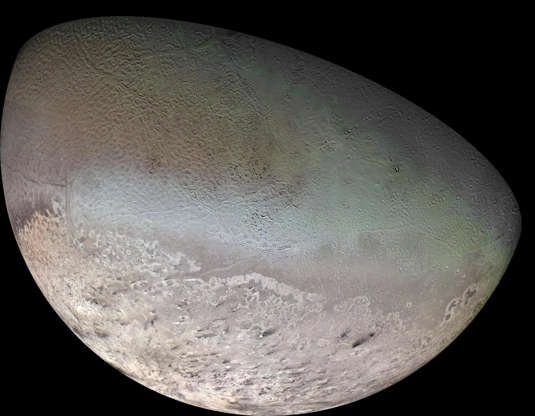
Neptune's largest moon, Triton is seen in this mosaic of images captured by Voyager 2 in 1989.
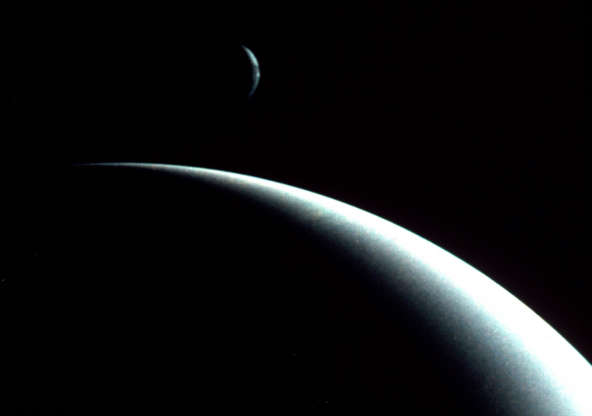


The crescents of Neptune and its moon Triton was acquired by Voyager II, approximately three days, six and a half hours after its closest approach to Neptune on Aug. 29, 1989.

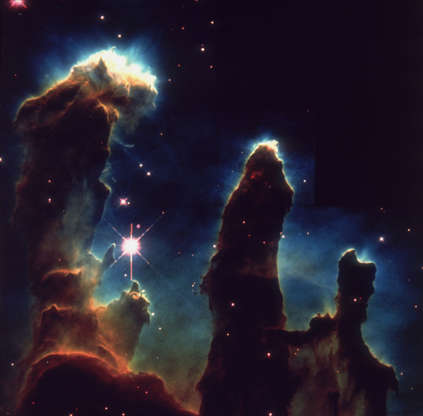
Gaseous pillars are seen in the Eagle Nebula in an image captured by Hubble Space Telescope in April 1995.
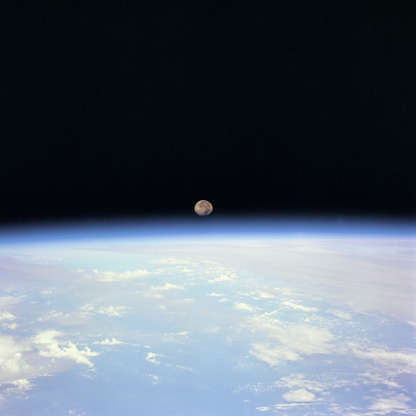


Moon sets over Earth in this image taken from space shuttle Discovery during STS-70 mission in July 1995.

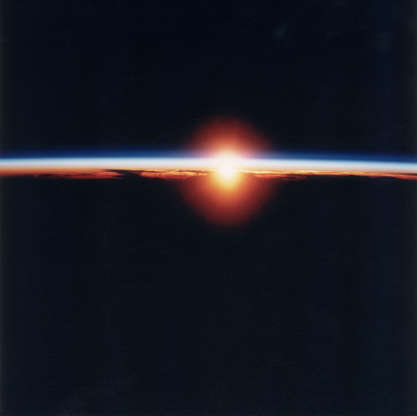
Sunrise over the West Indies, as seen from the space shuttle Discovery during NASA's STS-70 mission in July 1995.

The Galileo probe enters the turbulent upper atmosphere of Jupiter with its heat shield below and a parachute above on Dec. 7, 1995. It was expected to relay around 75 minutes of information to earth, before succumbing to the surrounding temperature and pressure. Behind it is the Galileo Orbiter, which was to remain above the cloud level to observe the Jupiter system from above.

The majestic spiral galaxy NGC 4414 as photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope in 1999.
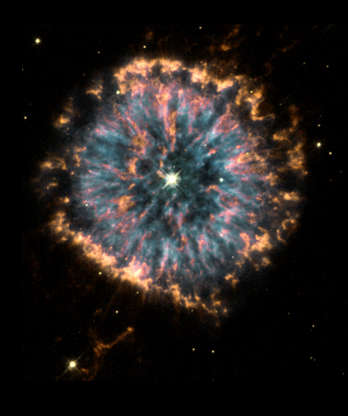

A giant celestial eye is seen in this image of planetary nebula NGC 6751 taken by Hubble Space Telescope in January 2000.
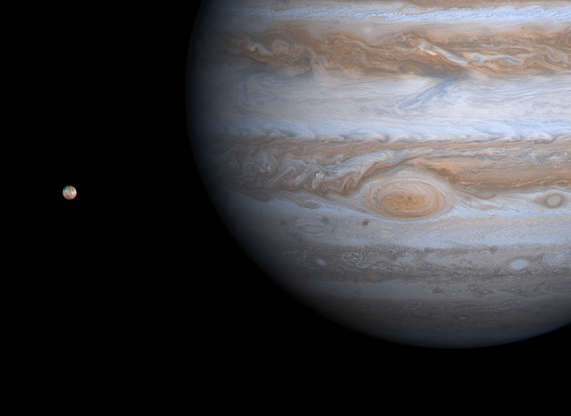


The Cassini spacecraft captured Jupiter's Great Red Spot and the volcanic moon Io (L) in this color composite image taken during its flyby from a distance of 17.8 million miles (28.6 million kilometers) in 2000.
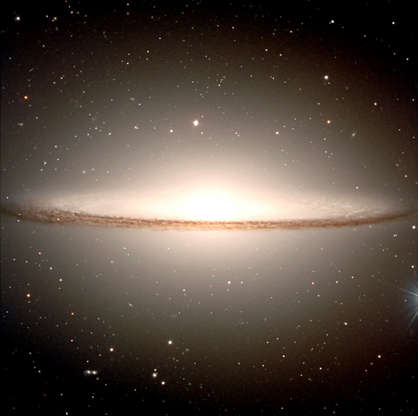


The Sombrero galaxy, located some 30 million light-years away, is seen in this NASA image taken Feb. 22, 2000.
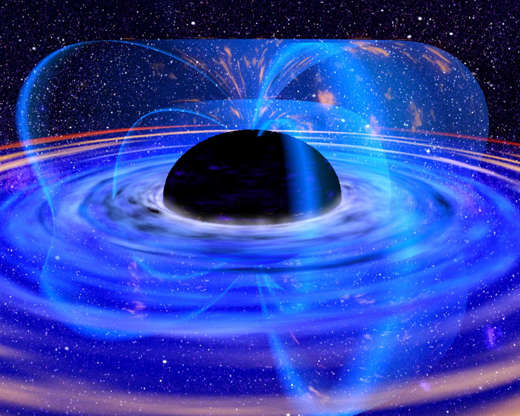


This ESA photograph released on Oct. 25, 2001, shows a supermassive black hole in the core of galaxy named MCG-6-30-15 as seen through the X-ray Multi-Mirror Mission (XMM-Newton) satellite. With this type of imaging, scientists for the first time saw energy being extracted from a black hole.
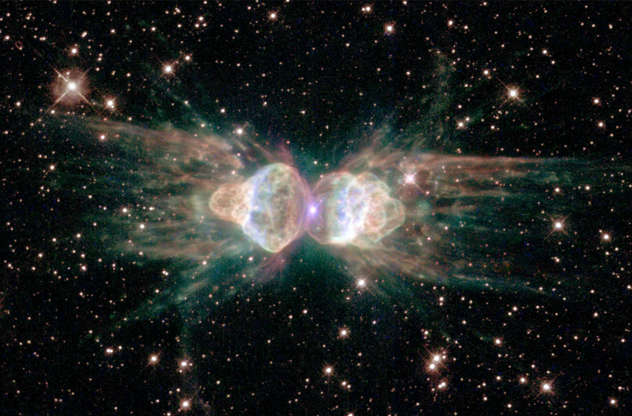


A picture of the celestial object called the Ant Nebula (a dying star) released by Hubble Space Telescope on Feb. 1, 2001.
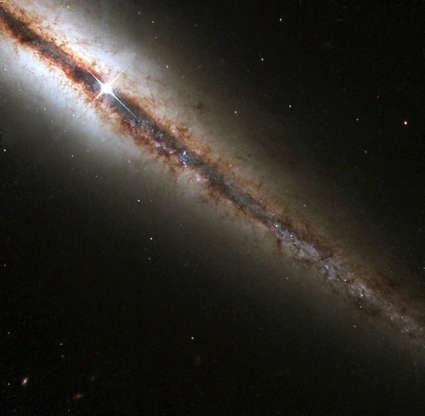


An image of the galaxy NGC 4013, located some 55 million light-years from Earth, taken by Hubble Space Telescope on March 1, 2001.
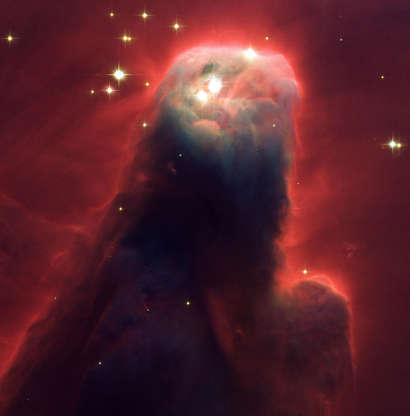


The Cone Nebula in an image taken by the new Advanced Camera for Surveys aboard Hubble Space Telescope in 2002.
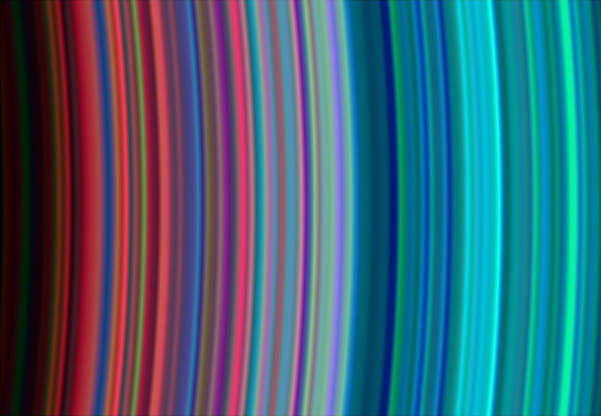


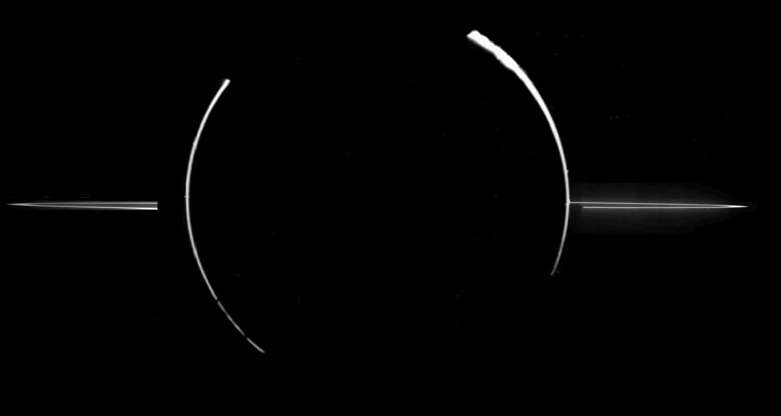
Saturn's rings are seen in this image taken by Cassini spacecraft on June 30, 2004.
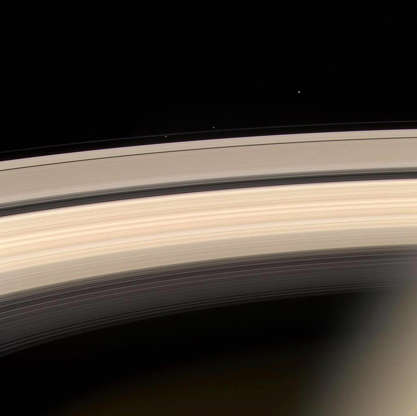


Saturn and its rings along with three of its moons (L-R) Prometheus, Pandora and Janus are prominently shown in this color image released by NASA’s Cassini aircraft on Aug. 19, 2004.
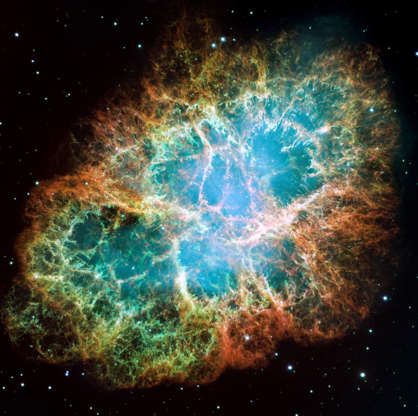


This mosaic image shows six-light-year-wide expanding remnant of a star's supernova explosion, Crab Nebula, taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and released on Dec. 2, 2005.
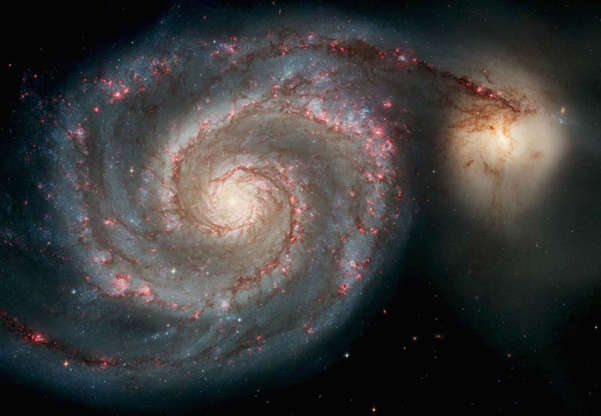


The Hubble Space Telescope released this image of Whirlpool Galaxy on April 25, 2005.


The panoramic view of Saturn and its rings captured by Cassini's wide-angle camera over nearly three hours on Sept. 15, 2006.
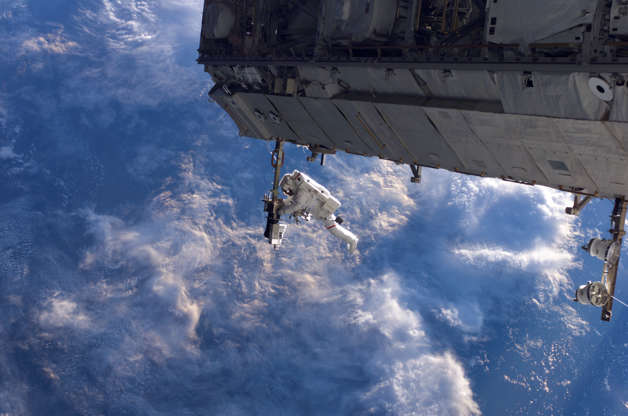


NASA astronaut Robert Curbeam works on the International Space Station's S1 truss during the space shuttle Discovery's STS-116 mission in December 2006. European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang (out of frame) was his partner in the six-hour, 36-minute spacewalk.


This image of the giant, active galaxy NGC 1275, released on Aug. 21, 2008, was taken using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys in July and August 2006. It provides amazing detail and resolution of fragile filamentary structures, which show up as a reddish lacy structure surrounding the central bright galaxy.

A planetary nebula named NGC 6302, also known as Butterfly Nebula and Bug Nebula, in the Scorpius constellation is captured on July 27, 2009. The image is provided by NASA, ESA and Hubble Space Telescope.
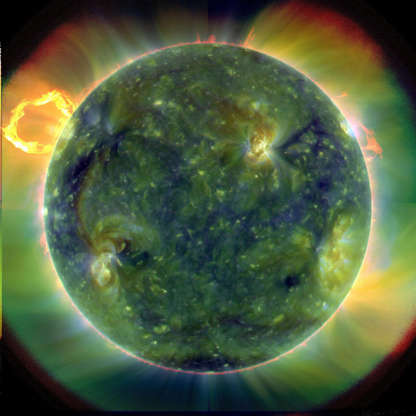

An extreme ultraviolet image of the Sun taken by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory on March 30, 2010.
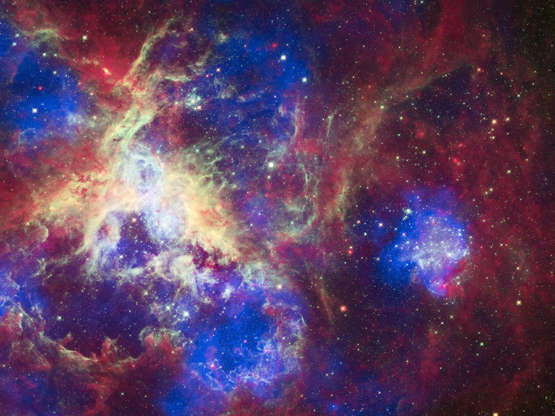


A composite view of Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy taken by Hubble Space Telescope on April 23, 2012.


The planet Venus at the start of its transit of the Sun on June 5, 2012.

The spinning vortex of Saturn's north polar storm is seen from Cassini spacecraft on Nov. 27, 2012. The photo released by NASA was taken from a distance of approximately 261,000 miles (420,038 kilometers) from Saturn.


A solar eruption rises above the surface of the sun on Dec. 31, 2012.

A deep look at the galaxy Centaurus A in May 2012.

The ring-like swirls of dust filling the Andromeda galaxy stand out colorfully in this image from the Herschel Space Observatory on Jan. 29, 2013.
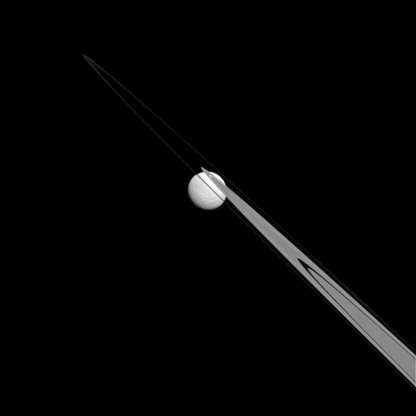


Tethys, one of Saturn's moons, is seen from a distance of approximately 1.1 million miles (1.8 million kilometers) from the Cassini spacecraft on July 14, 2014.
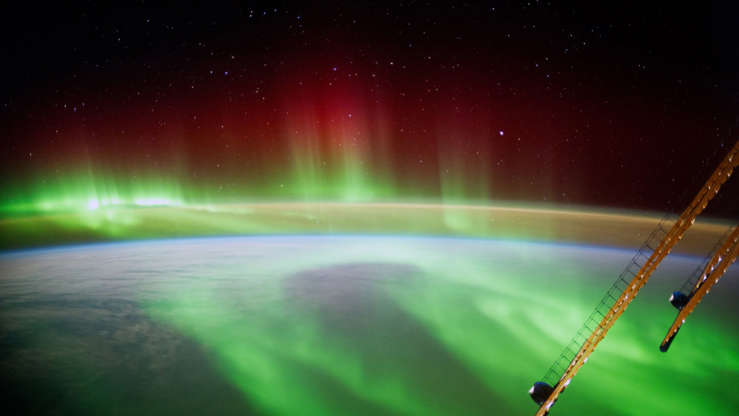


German ESA astronaut Alexander Gerst took this image of an aurora as he circled Earth while aboard the International Space Station (ISS) on Sept. 9, 2014.
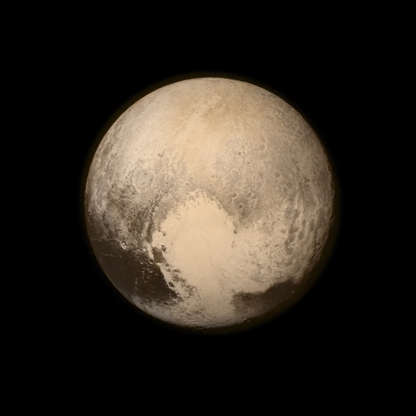


An image of Pluto by NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft during its flyby on July 13, 2015, taken from a distance of 476,000 miles (766,000 kilometers) from the surface.


A satellite image shows the far side of the moon as it crosses between the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) spacecraft and the Earth. The image was released on Aug. 5, 2015.

An undated image of Hale Crater taken by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Scientists reported on Sept. 28, 2015, that the narrow streaks on the slopes could have been formed by saline water.
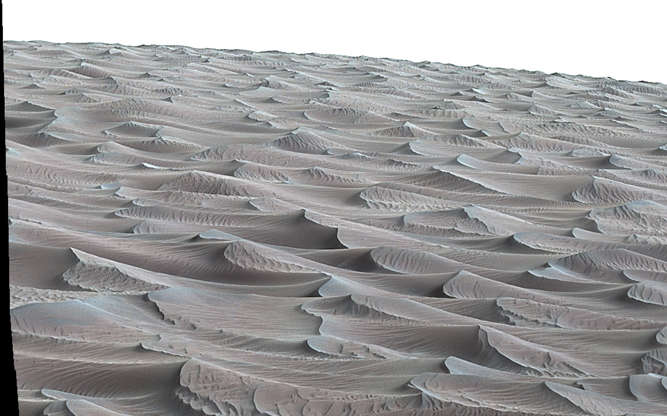


An image of the Martian rippled surface called Bagnold Dunes, taken by NASA's Curiosity rover on Nov. 27, 2015.
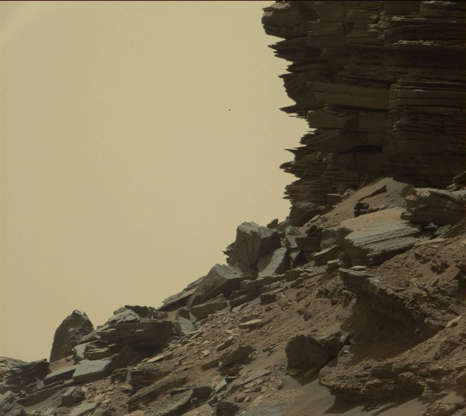


A view of the hillside outcrop with layered rocks in the Murray Buttes region on Mars taken by NASA's Curiosity rover on Sept. 8, 2016.
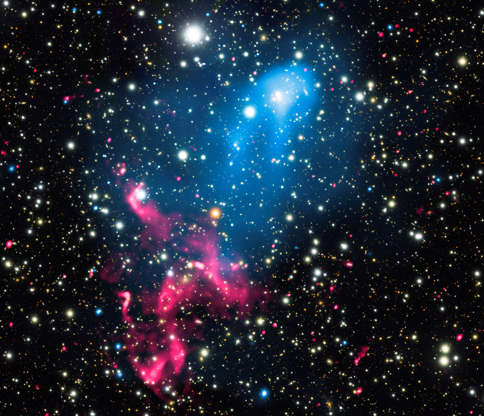


A composite image, released by NASA on Jan. 5, 2017, contains X-rays from Chandra (blue), radio emission from the GMRT (red), and optical data from Subaru (red, green, and blue) of the colliding galaxy clusters called Abell 3411 and Abell 3412.
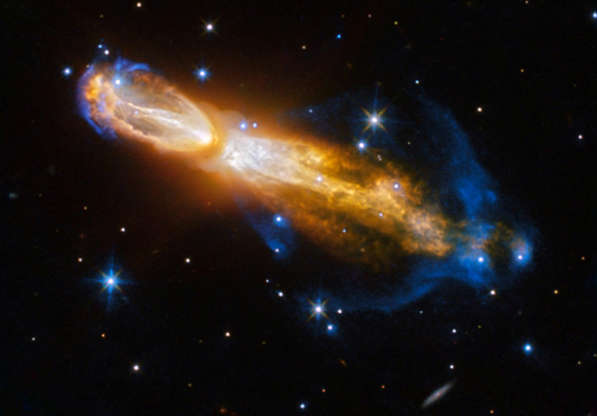


The Calabash Nebula in an image released by NASA on Feb. 3, 2017. Taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, it shows the star transforming from a red giant to a planetary nebula, as it blows gas and dust out into the surrounding space.
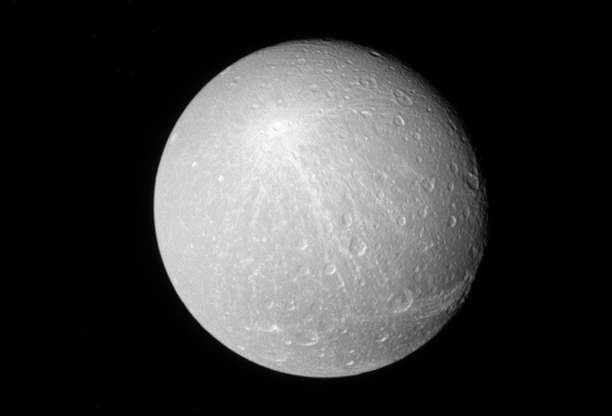


A view of Saturn’s moon Dione released by NASA on Feb. 21, 2017.
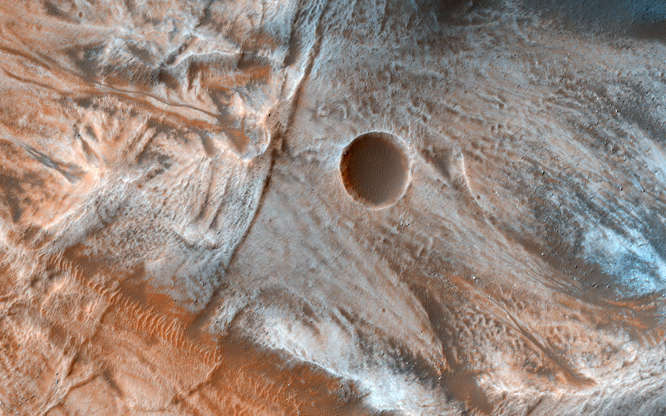


A view of the surface of Mars released by NASA on March 7, 2017, shows viscous, lobate flow features commonly found at the bases of slopes in the mid-latitudes of the planet.
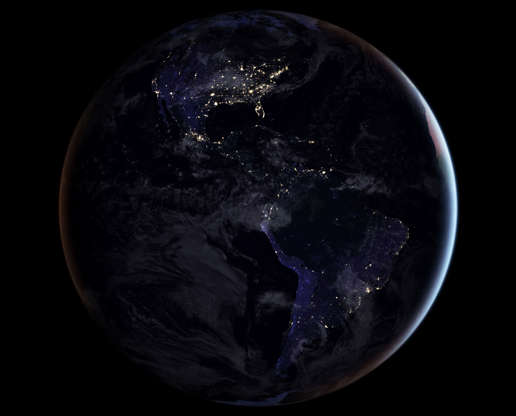

A composite image released by NASA on April 12, 2017, showing the Earth's full western hemisphere at night. This map of night lights is based on imagery from 2016.
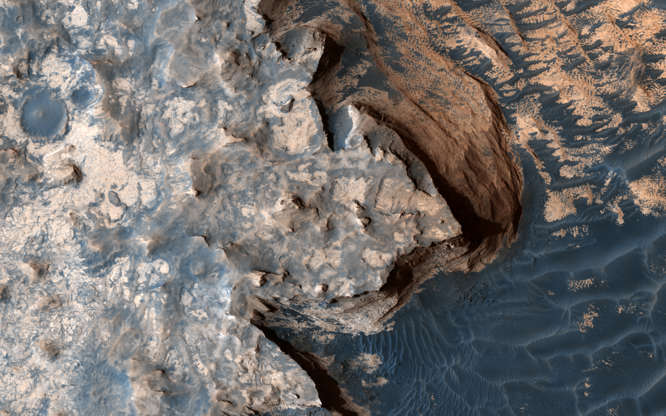


An image acquired by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment camera on April 18, 2017, shows a rugged cliff edge on Mars. The image was released on June 22.
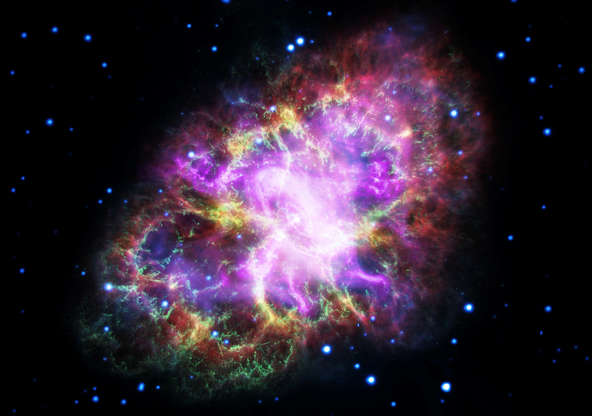


This composite image of the Crab Nebula, a supernova remnant, was assembled by combining data from five telescopes spanning nearly the entire breadth of the electromagnetic spectrum: the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array, the Spitzer Space Telescope, the Hubble Space Telescope, the XMM-Newton Observatory, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory. The photo was released on May 10, 2017.
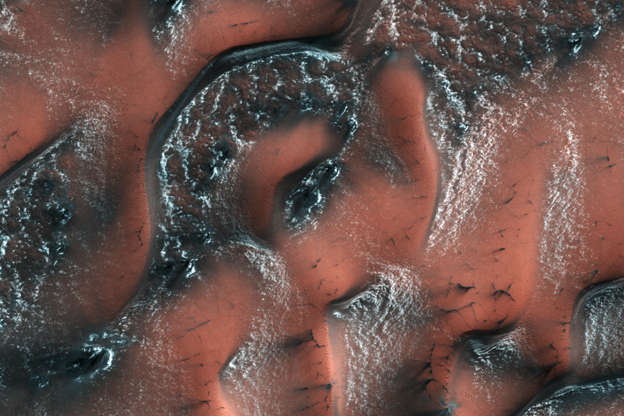


An image taken by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows spring in the northern hemisphere of the planet on May 21, 2017.
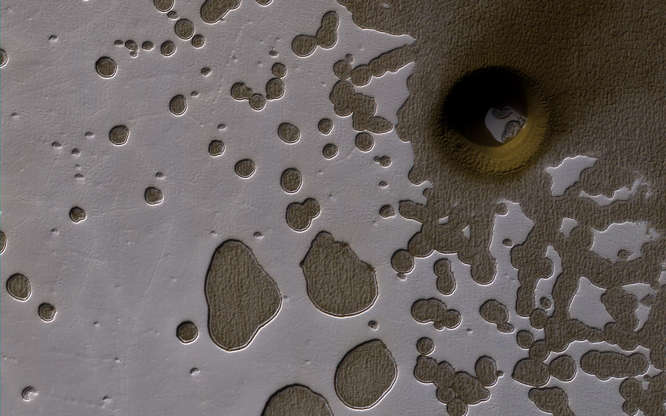


A late summer view of the southern hemisphere of Mars is seen in this image taken from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and released on June 2, 2017. Shallow pits are seen in the bright residual cap of carbon dioxide ice. There is also a deeper, circular formation that penetrates through the ice and dust, possibly an impact crater or a collapse pit.
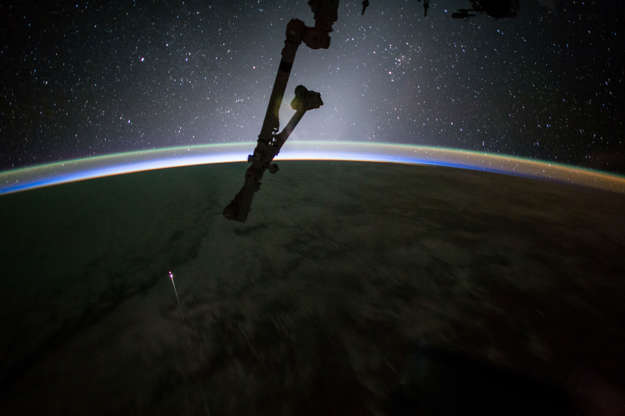


The SpaceX Dragon capsule re-entered Earth's atmosphere before splashing down in the Pacific Ocean west of Baja California, Mexico, on July 3, 2017, in this photograph by NASA astronaut Jack Fischer.
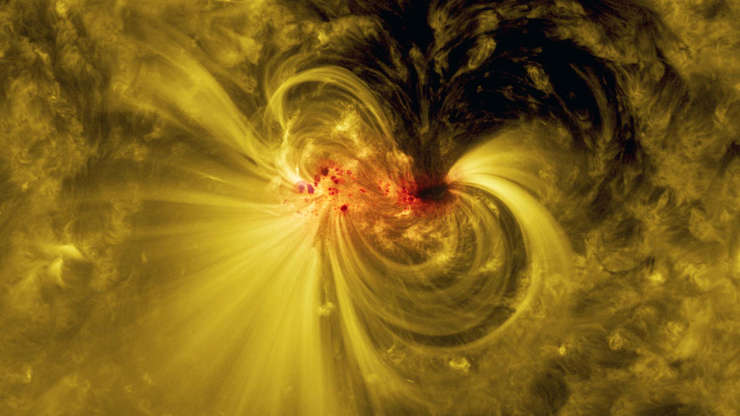


An image showing an area of active magnetic fields on the sun, captured by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory on July 5, 2017.


Jupiter's Great Red Spot fades from view while the dynamic bands of the southern region come into focus, in this image taken on July 10, 2017, from the JunoCam imager on NASA's Juno spacecraft. North is to the left of the image, and south is on the right.
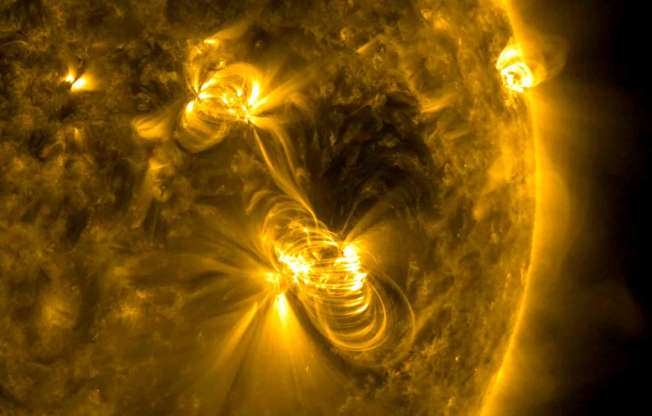


A medium-sized solar flare and a coronal mass ejection erupting from the same large active region of the sun on July 14, 2017.


A picture taken with a telescope shows the Orion Nebula in the sky over the Hanthawaddy golf course in Bago, Myanmar, on Dec. 24, 2017.
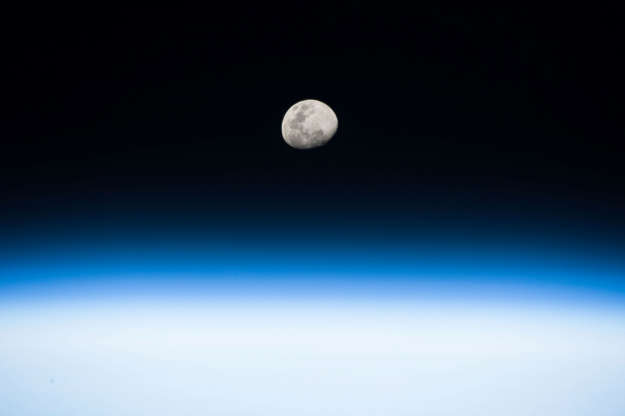


The moon rises in this photo, taken in low Earth orbit by NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik from the International Space Station on Aug. 3, 2017.
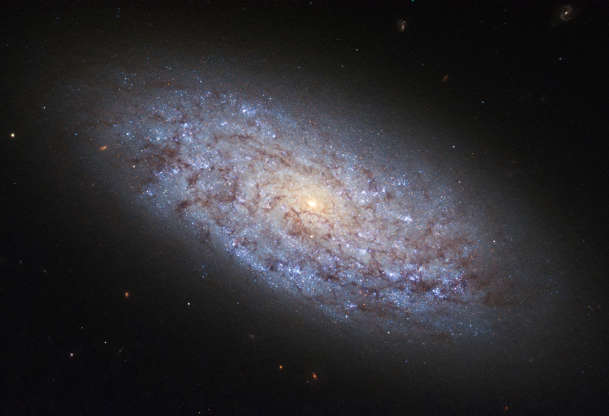


The dwarf galaxy named NGC 5949 is seen in this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image released on Aug. 11, 2017.
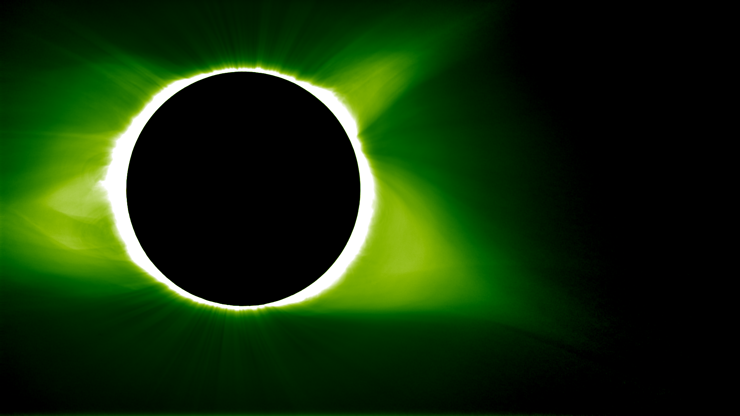


A total solar eclipse, which provided scientists with a rare chance to investigate the sun and its influence on Earth, as seen on Aug. 21, 2017.
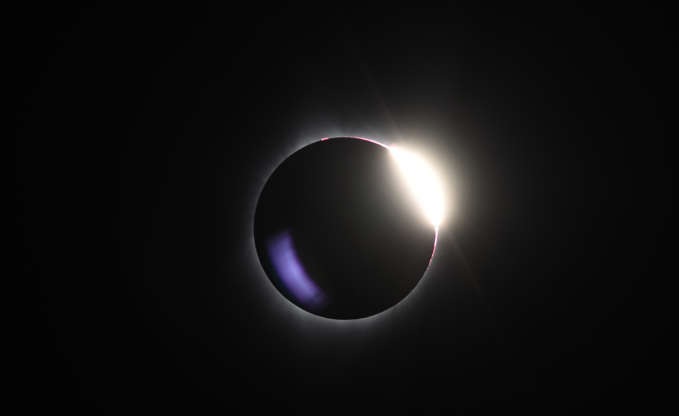


The diamond ring effect is visible as the moon passes in front of the sun during a total solar eclipse seen from the Big Summit Prairie ranch in Ochoco National Forest near Mitchell, Oregon, U.S., on Aug. 21, 2017.
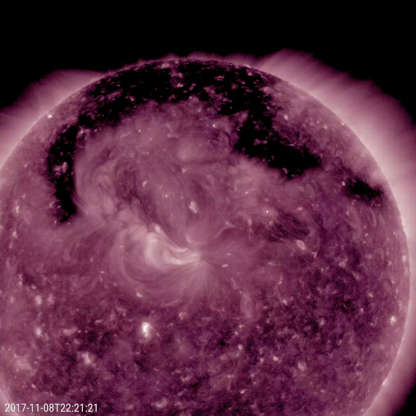

Coronal holes on the sun are shown in this image from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory during Nov. 7-9, 2017.


Swirling cloud formations in the northern area of Jupiter's north temperate belt are seen in this color-enhanced image taken by Juno on Feb. 7, 2018.
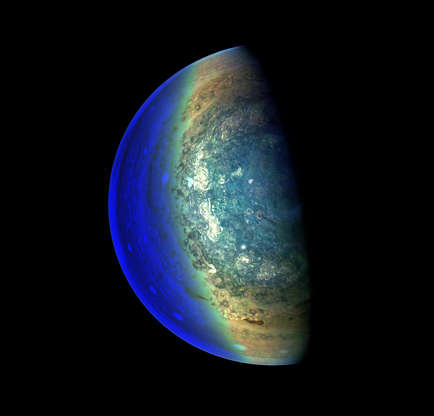

This image captures the swirling cloud formations around the south pole of Jupiter, looking up toward the equatorial region. NASA’s Juno spacecraft took the color-enhanced image during its 11th close flyby of the gas giant planet on Feb. 7, 2018.
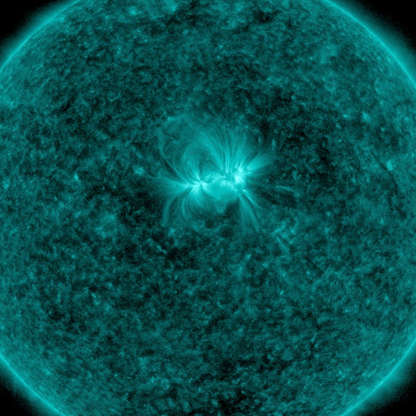


The lone active region visible on our Sun put on a fine display with its tangled magnetic field lines swaying and twisting above it (April 24-26, 2018) when viewed in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light.
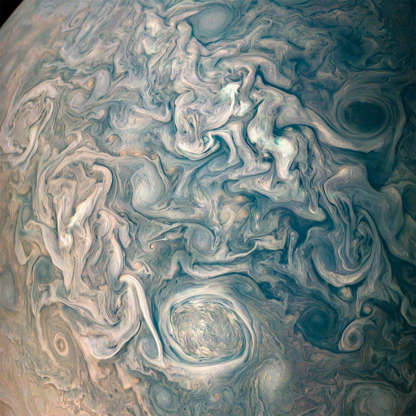


Swirling cloud belts and tumultuous vortices within Jupiter’s northern hemisphere are shown in this image from Juno spacecraft on May 23, 2018.
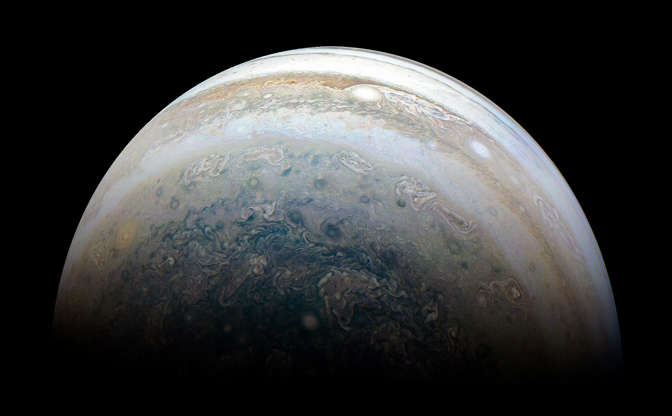


The color-enhanced image was taken on May 23, 2018, as NASA's Juno spacecraft performed its 13th close flyby of Jupiter.

The first image ever produced of a black hole, taken by the Event Horizon Telescope on April 10, 2019 and observed at the center of Messier 87 in the Virgo galaxy cluster. The telescope was designed specifically to capture images of black holes, through a planet-scale array of eight ground-based radio telescopes around the world.
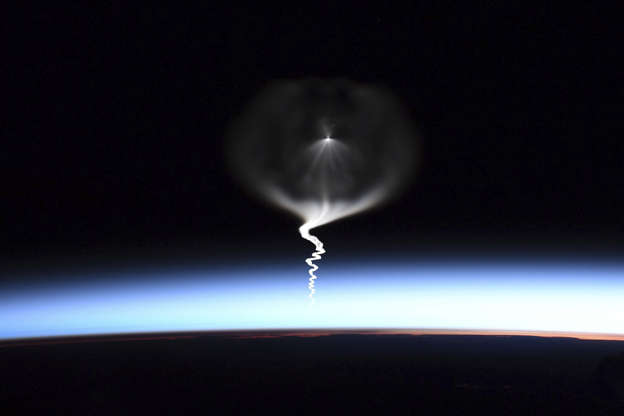


This image by NASA astronaut Christina Koch shows the launch of a Russian Soyuz rocket, as seen from the International Space Station, during its approach on Sept. 25, 2019.
I think we can agree that the verse quoted at the start is true! (Unless you're a Flat Earther, and deny the glory of the heavens.)
Comments
Post a Comment